Problem statement
Given the head of a linked list and an integer val, remove all the nodes of the linked list that has Node.val == val, and return the new head.
Example 1
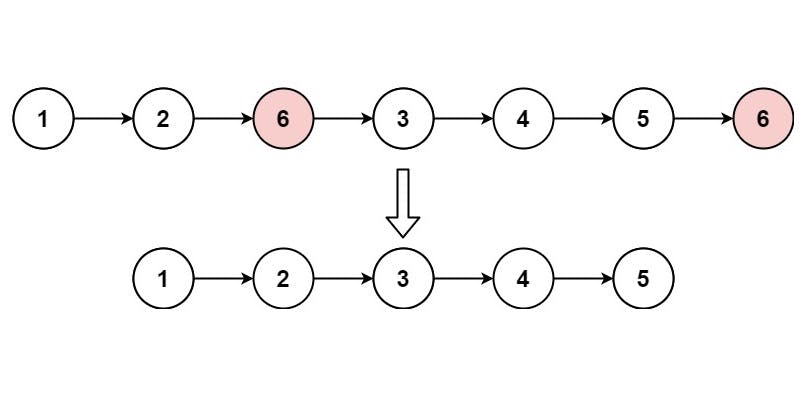
Input: head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 2
Input: head = [], val = 1
Output: []
Example 3
Input: head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
Output: []
Constraints
The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 10^4].1 <= Node.val <= 50.0 <= val <= 50.
Linked list data structure
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
Solution 1: Consider the special case for head
Removing a node A in a linked list means instead of connecting the previous node A.pre to A, you connect A.pre to A.next.
Code
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
while (head && head->val == val) {
head = head->next;
}
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* pre = head;
while (pre->next) {
if (pre->next->val == val) {
pre->next = pre->next->next;
} else {
pre = pre->next;
}
}
return head;
}
void print(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* node = head;
std::cout << "[";
while (node) {
std::cout << node->val << ",";
node = node->next;
}
std::cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
ListNode sixb(6);
ListNode five(5, &sixb);
ListNode four(4, &five);
ListNode three(3, &four);
ListNode sixa(6, &three);
ListNode two(2, &sixa);
ListNode head(1, &two);
ListNode* newHead = removeElements(&head, 6);
print(newHead);
newHead = removeElements(nullptr, 1);
print(newHead);
ListNode seven4(7);
ListNode seven3(7, &seven4);
ListNode seven2(7, &seven3);
ListNode seven1(7, &seven2);
newHead = removeElements(&seven1, 7);
print(newHead);
}
Output:
[1,2,3,4,5,]
[]
[]
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N), whereNis the number of nodes.Memory:
O(1).
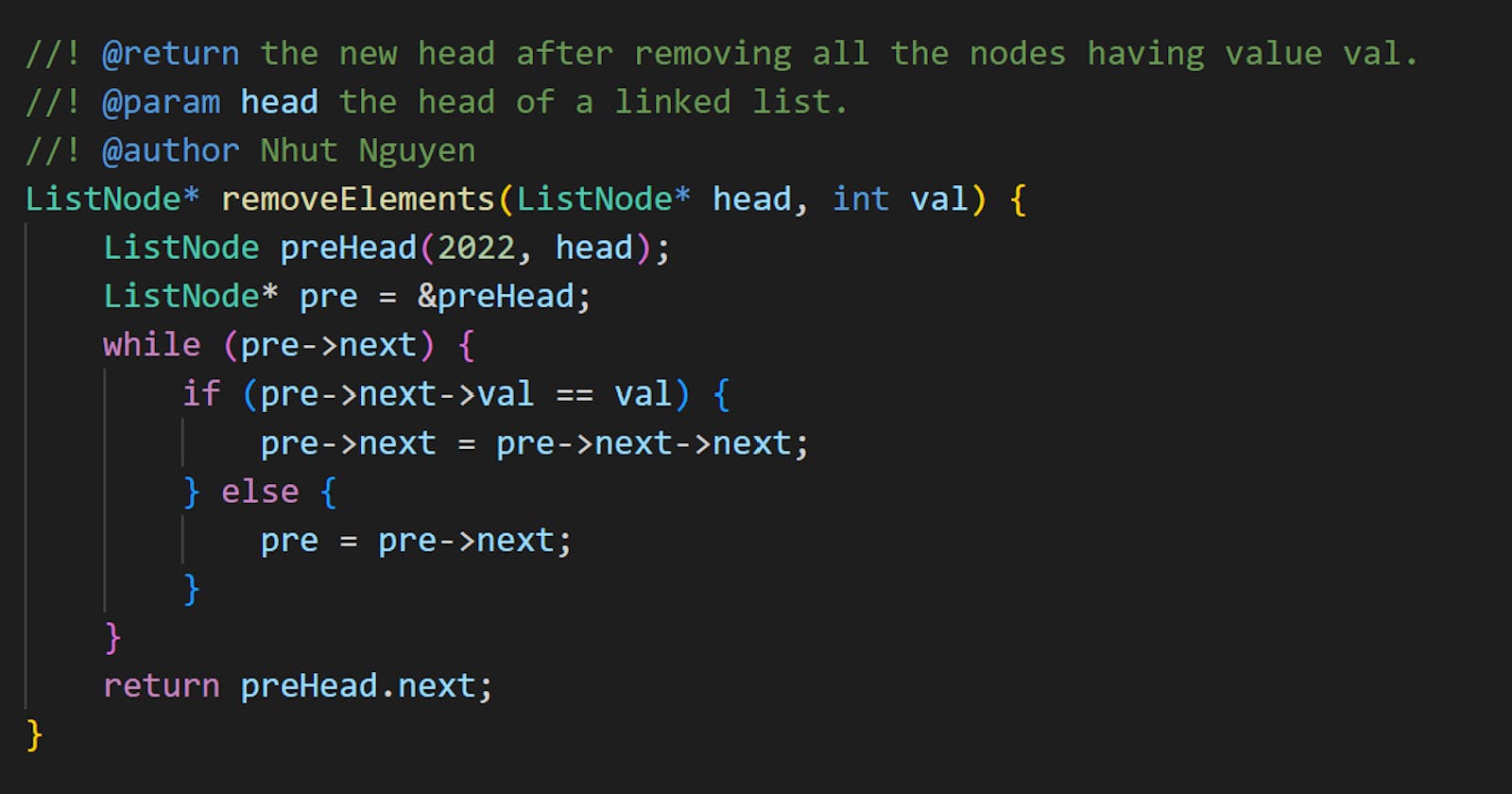
Solution 2: Create a previous dummy node for head
head has no pre. You can create a dummy node for head.pre.
Code
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode preHead(2023, head);
ListNode* pre = &preHead;
while (pre->next) {
if (pre->next->val == val) {
pre->next = pre->next->next;
} else {
pre = pre->next;
}
}
return preHead.next;
}
void print(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* node = head;
std::cout << "[";
while (node) {
std::cout << node->val << ",";
node = node->next;
}
std::cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
ListNode sixb(6);
ListNode five(5, &sixb);
ListNode four(4, &five);
ListNode three(3, &four);
ListNode sixa(6, &three);
ListNode two(2, &sixa);
ListNode head(1, &two);
ListNode* newHead = removeElements(&head, 6);
print(newHead);
newHead = removeElements(nullptr, 1);
print(newHead);
ListNode seven4(7);
ListNode seven3(7, &seven4);
ListNode seven2(7, &seven3);
ListNode seven1(7, &seven2);
newHead = removeElements(&seven1, 7);
print(newHead);
}
Output:
[1,2,3,4,5,]
[]
[]
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N), whereNis the number of nodes.Memory:
O(1).
Attention!
Depending on your real situation, in practice, you might need to deallocate memory for the removed nodes; especially when they were allocated by the new operator.
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode preHead(2022, head);
ListNode* pre = &preHead;
while (pre->next) {
if (pre->next->val == val) {
ListNode* node = pre->next;
pre->next = node->next;
delete node;
} else {
pre = pre->next;
}
}
return preHead.next;
}
Key takeaway
In some linked list problems where
headneeds to be treated as a special case, you can create a previous dummy node for it to adapt the general algorithm.Be careful with memory leak when removing nodes of the linked list containing pointers.
References
Thanks for reading. Feel free to share your thought about my content and check out my FREE book “10 Classic Coding Challenges”.