Problem statement
The Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted F(n) form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2), for n > 1.
Given n, calculate F(n).
Example 1
Input: n = 2
Output: 1
Explanation: F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1.
Example 2
Input: n = 3
Output: 2
Explanation: F(3) = F(2) + F(1) = 1 + 1 = 2.
Example 3
Input: n = 4
Output: 3
Explanation: F(4) = F(3) + F(2) = 2 + 1 = 3.
Constraints
0 <= n <= 30.
Solution 1: Recursive
#include <iostream>
int fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
int main() {
std::cout << fib(2) << std::endl;
std::cout << fib(3) << std::endl;
std::cout << fib(4) << std::endl;
}
Output:
1
2
3
Complexity
Runtime:
O(2^n).Extra space:
O(2^n).
Solution 2: Dynamic programming
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
std::vector<int> f(n + 1);
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
int main() {
std::cout << fib(2) << std::endl;
std::cout << fib(3) << std::endl;
std::cout << fib(4) << std::endl;
}
Output:
1
2
3
Complexity
Runtime:
O(n).Extra space:
O(n).
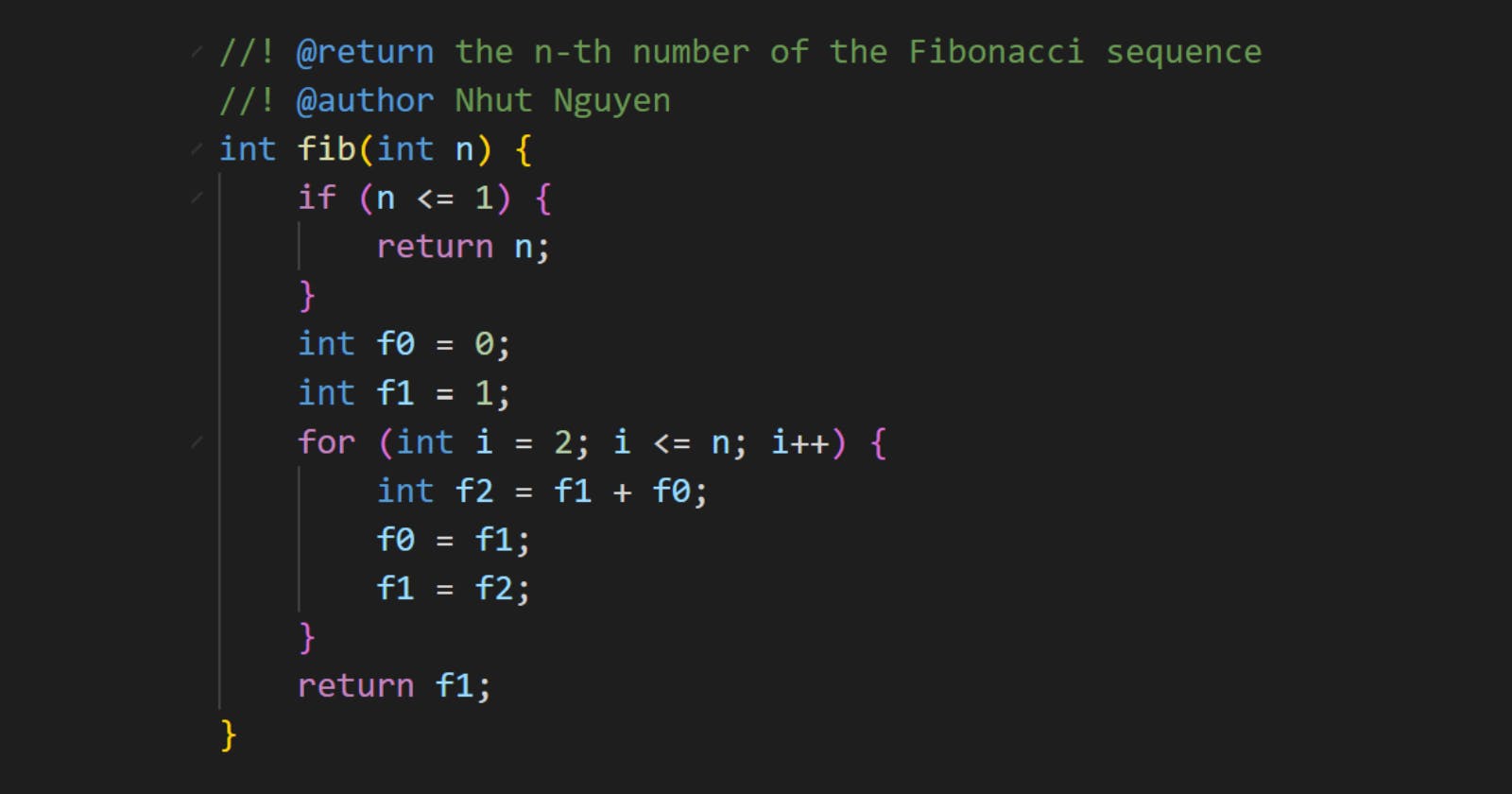
Solution 3: Reduce space for dynamic programming
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
int f0 = 0;
int f1 = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int f2 = f1 + f0;
f0 = f1;
f1 = f2;
}
return f1;
}
int main() {
std::cout << fib(2) << std::endl;
std::cout << fib(3) << std::endl;
std::cout << fib(4) << std::endl;
}
Output:
1
2
3
Complexity
Runtime:
O(n).Extra space:
O(1).
You can try to solve this problem by yourself at leetcode.com/problems/fibonacci-number
Thanks for reading. Feel free to share your thought about my content and check out my FREE book “10 Classic Coding Challenges”.