Problem statement
The Hamming distance between two integers is the number of positions at which the corresponding bits are different.
Given two integers x and y, return the Hamming distance between them.
Example 1
Input: x = 1, y = 4
Output: 2
Explanation:
1 (0 0 0 1)
4 (0 1 0 0)
↑ ↑
The above arrows point to positions where the corresponding bits are different.
Example 2
Input: x = 3, y = 1
Output: 1
Constraints
0 <= x, y <= 2^31.
Solution: Using bitwise operator XOR
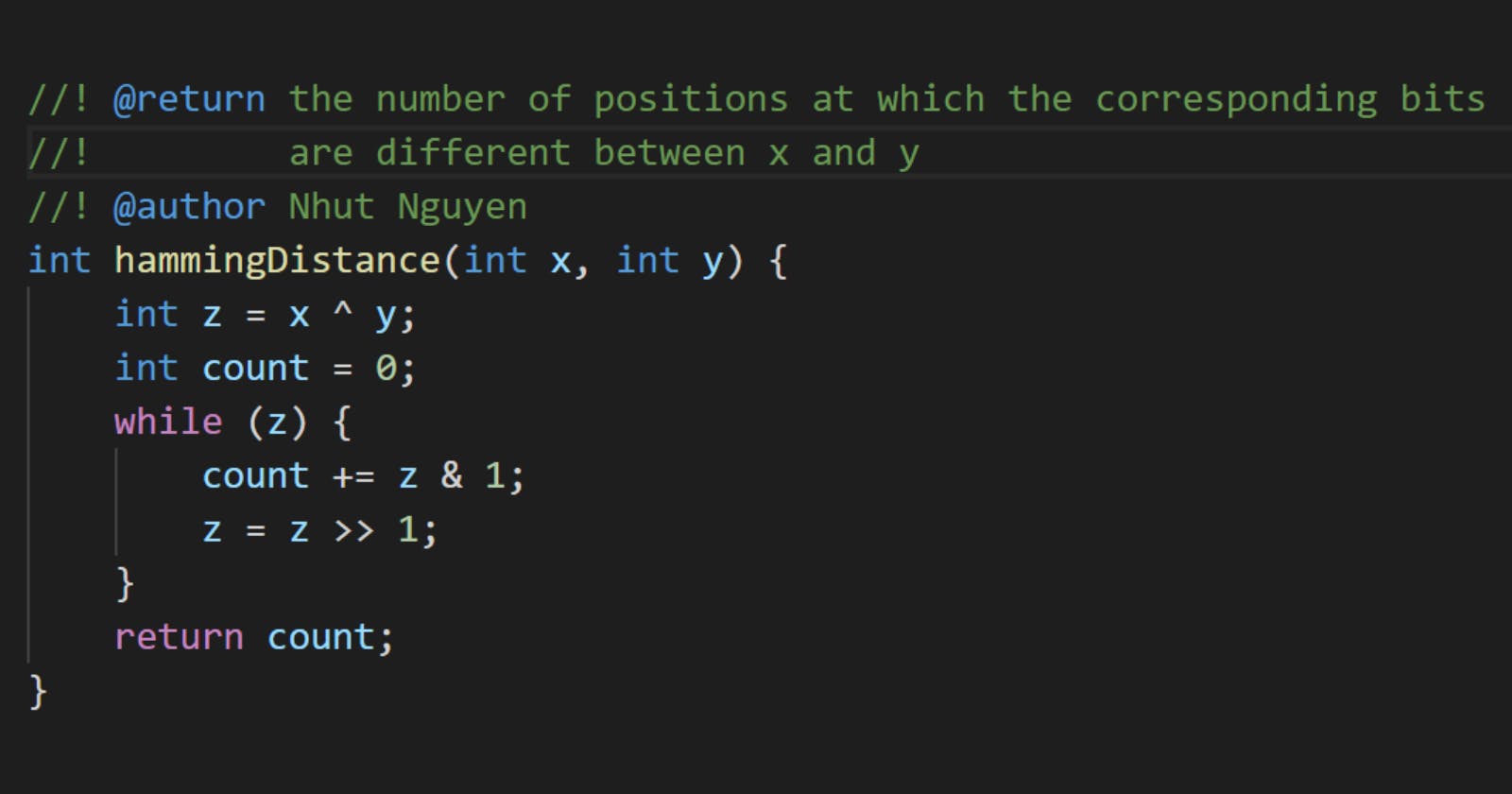
You could use bit operator ^ (XOR) to get the bit positions where x and y are different. Then use bit operator & (AND) at each position to count them.
Code
#include <iostream>
int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int z = x ^ y;
int count = 0;
while (z) {
count += z & 1;
z = z >> 1;
}
return count;
}
int main() {
std::cout << hammingDistance(1,4) << std::endl;
std::cout << hammingDistance(1,3) << std::endl;
}
Output:
2
1
Complexity
Runtime:
O(1).Extra space:
O(1).
References
Thanks for reading. Feel free to share your thought about my content and check out my FREE book “10 Classic Coding Challenges”.