Problem statement
Given a string array words, return the maximum value of length(word[i]) * length(word[j]) where the two words do not share common letters. If no such two words exist, return 0.
Example 1
Input: words = ["abcw","baz","foo","bar","xtfn","abcdef"]
Output: 16
Explanation: The two words can be "abcw", "xtfn".
Example 2
Input: words = ["a","ab","abc","d","cd","bcd","abcd"]
Output: 4
Explanation: The two words can be "ab", "cd".
Example 3
Input: words = ["a","aa","aaa","aaaa"]
Output: 0
Explanation: No such pair of words.
Constraints
2 <= words.length <= 1000.1 <= words[i].length <= 1000.words[i]consists only of lowercase English letters.
Solution 1: Bruteforce
For each words[i], for all words[j] with j > i, check if they do not share common letters and compute the product of their lengths.
Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int maxProduct(vector<string>& words) {
int maxP = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {
vector<bool> visited(26, false);
for (char c : words[i]) {
visited[c - 'a'] = true;
}
for (int j = i + 1; j < words.size(); j++) {
bool found = false;
for (char c : words[j]) {
if (visited[c - 'a']) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
maxP = max(maxP, (int) (words[i].length() * words[j].length()));
}
}
}
return maxP;
}
int main() {
vector<string> words{"abcw","baz","foo","bar","xtfn","abcdef"};
cout << maxProduct(words) << endl;
words = {"a","ab","abc","d","cd","bcd","abcd"};
cout << maxProduct(words) << endl;
words = {"a","aa","aaa","aaaa"};
cout << maxProduct(words) << endl;
}
Output:
16
4
0
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N^2**M), whereN = words.length,M = avg(words[i].length).Extra space:
O(1).
Solution 2: Checking common letters using bit masking
You can map a words[i] to the bit representation of an integer n by their characters like the following:
If the word
words[i]contains the letter'a', the bit at position0ofnis1.If the word
words[i]contains the letter'b', the bit at position1ofnis1....
If the word
words[i]contains the letter'z', the bit at position25ofnis1.
Then to check if two words have common letters, you just perform the bitwise operator AND on them.
For Example 1:
The word
"abcw"is mapped to00010000000000000000000111.The word
"baz"is mapped to10000000000000000000000011."abcw" & "baz" = 00000000000000000000000011. This value is not zero, which means they have common letters.
This technique is called bit masking.
Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
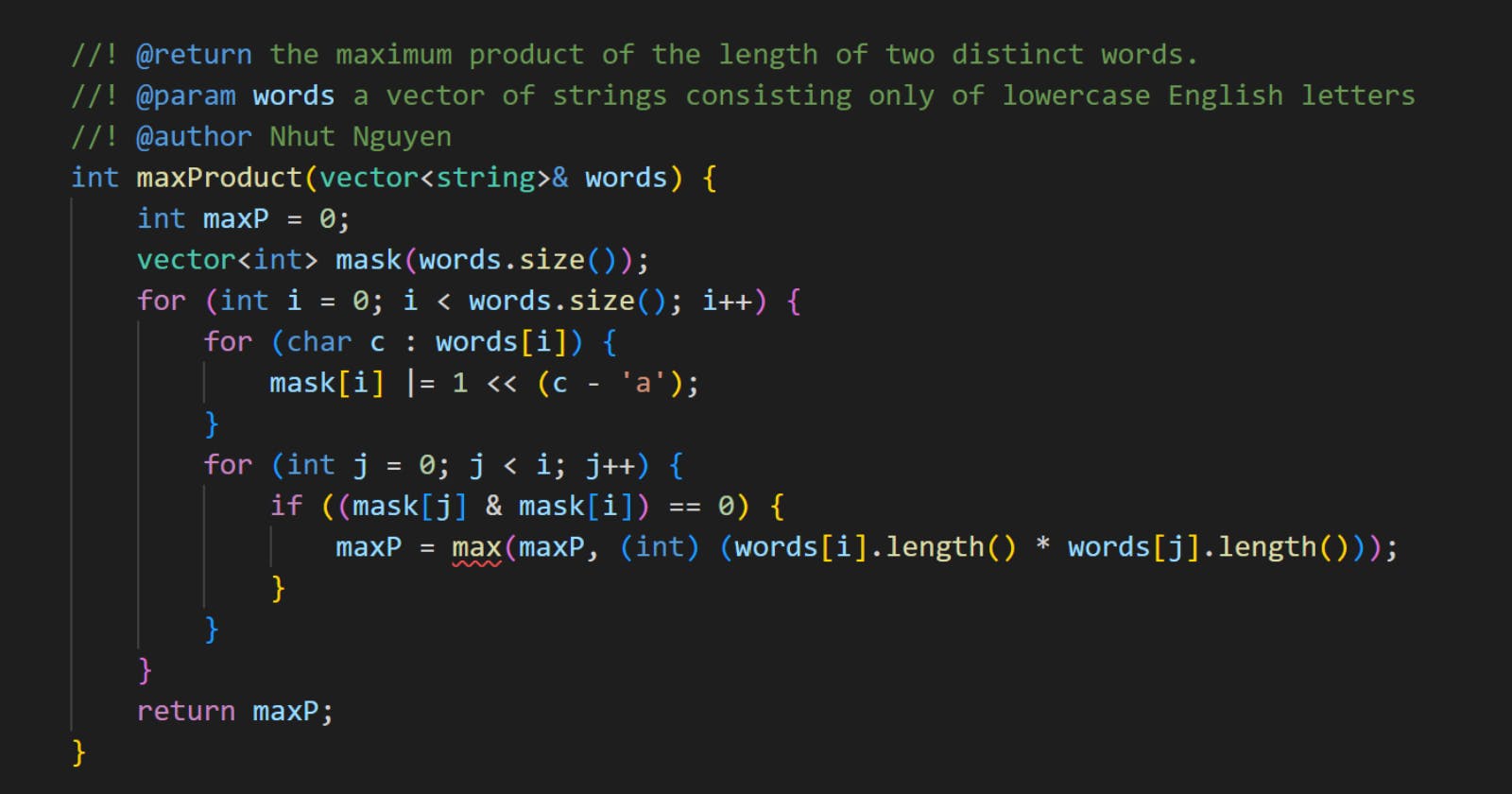
int maxProduct(vector<string>& words) {
int maxP = 0;
vector<int> mask(words.size());
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {
for (char c : words[i]) {
mask[i] |= 1 << (c - 'a');
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if ((mask[j] & mask[i]) == 0) {
maxP = max(maxP, (int) (words[i].length() * words[j].length()));
}
}
}
return maxP;
}
int main() {
vector<string> words{"abcw","baz","foo","bar","xtfn","abcdef"};
cout << maxProduct(words) << endl;
words = {"a","ab","abc","d","cd","bcd","abcd"};
cout << maxProduct(words) << endl;
words = {"a","aa","aaa","aaaa"};
cout << maxProduct(words) << endl;
}
Output:
16
4
0
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N^2), whereN = words.length.Extra space:
O(N).
References
Thanks for reading. Feel free to share your thought about my content and check out my FREE book “10 Classic Coding Challenges”.