Problem statement
Given the starting nodes of two sorted linked lists, list1 and list2, your task is to combine these lists into a single sorted linked list.
This merged list should be created by connecting the nodes from both list1 and list2. Finally, you should return the starting node of the resulting merged linked list.
Example 1
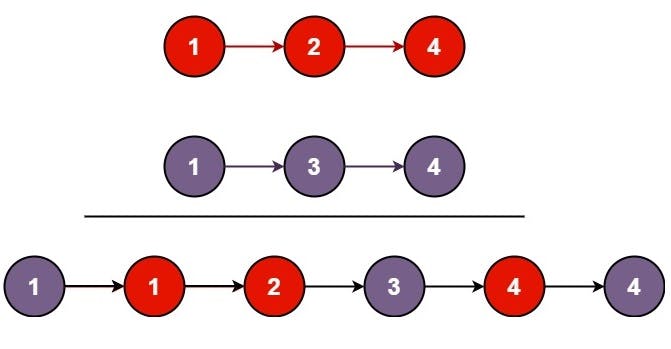
Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
Example 2
Input: list1 = [], list2 = []
Output: []
Example 3
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints
The number of nodes in both lists is in the range
[0, 50].-100 <= Node.val <= 100.Both
list1andlist2are sorted in non-decreasing order.
Solution: Constructing a new list
For each pair of nodes between the two lists, pick the node having a smaller value to append to the new list.
Code
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if (list1 == nullptr) {
return list2;
} else if (list2 == nullptr) {
return list1;
}
// identify which list is head
ListNode* head = list1;
if (list2->val < head->val) {
head = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
} else {
list1 = list1->next;
}
ListNode* node = head;
while (list1 && list2) {
if (list1->val < list2->val) {
node->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
} else {
node->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
node = node->next;
}
if (list1 == nullptr) {
node->next = list2;
} else {
node->next = list1;
}
return head;
}
void printResult(ListNode* head) {
std::cout << "[";
while (head) {
std::cout << head->val << ",";
head = head->next;
}
std::cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
ListNode four1(4);
ListNode two1(2, &four1);
ListNode one1(1, &two1);
ListNode four2(4);
ListNode three2(3, &four2);
ListNode one2(1, &three2);
auto newOne = mergeTwoLists(&one1, &one2);
printResult(newOne);
auto empty = mergeTwoLists(nullptr, nullptr);
printResult(empty);
ListNode zero(0);
auto z = mergeTwoLists(nullptr, &zero);
printResult(z);
}
Output:
[1,1,2,3,4,4,]
[]
[0,]
Code explanation
The function begins with two base cases to handle situations where one of the input lists is empty:
If
list1is empty (i.e.,list1isnullptr), the function simply returnslist2. There is no need to merge anything becauselist1is empty.Similarly, if
list2is empty (i.e.,list2isnullptr), the function returnslist1.
A
headpointer will be used to keep track of the merged list. The code determines which oflist1andlist2should be the head of the merged list. It does this by comparing the values of the first nodes inlist1andlist2:If the value of the first node in
list2is less than the value of the first node inlist1, it means thatlist2should be the new head of the merged list. The code updates theheadpointer to point tolist2, and it advances thelist2pointer to the next node.If the value of the first node in
list1is less than or equal to the value inlist2,list1should be the new head. The code advances thelist1pointer to the next node.
The main merging process is performed using a
whileloop that continues as long as bothlist1andlist2are not empty:Inside the loop, the code compares the values of the first nodes in
list1andlist2:If the value in
list1is smaller, the code connects the current node pointed to bynodeto the node inlist1, and advanceslist1to its next node.If the value in
list2is smaller or equal, the code connects the current node pointed to bynodeto the node inlist2, and advanceslist2to its next node.
After connecting a node, the
nodepointer is moved to the newly connected node.
After the
whileloop completes, one of the input lists may still have remaining elements. To ensure that all elements are included in the merged list, the code appends the remaining nodes from eitherlist1orlist2(whichever is not empty) to the end of the merged list.Finally, the function returns
head, which points to the head of the merged sorted linked list.
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N), whereN = list1.length + list2.length.Extra space:
O(1).
Thanks for reading. Feel free to share your thought about my content and check out my FREE book 10 Classic Coding Challenges.

