Problem statement
Given a non-empty array of integers nums, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.
Example 1
Input: nums = [2,2,1]
Output: 1
Example 2
Input: nums = [4,1,2,1,2]
Output: 4
Example 3
Input: nums = [1]
Output: 1
Constraints
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4.-3 * 10^4 <= nums[i] <= 3 * 10^4.Each element in the array appears twice except for one element which appears only once.
Solution 1: Counting the appearances
Count how many times each element appears in the array. Then return the one appearing only once.
Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> count;
for (int n : nums) {
count[n]++;
}
int single;
for (auto& pair : count) {
if (pair.second == 1) {
single = pair.first;
break;
}
}
return single;
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums{2,2,1};
cout << singleNumber(nums) << endl;
nums = {4,1,2,1,2};
cout << singleNumber(nums) << endl;
nums = {1};
cout << singleNumber(nums) << endl;
}
Output:
1
4
1
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N), whereN = nums.length.Extra space:
O(N)(not constant, need another solution).
Solution 2: Bitwise exclusive OR
You can also use the bitwise XOR operator to cancel out the duplicated elements in the array. The remain element is the single one.
a XOR a = 0.
a XOR 0 = a.
Code
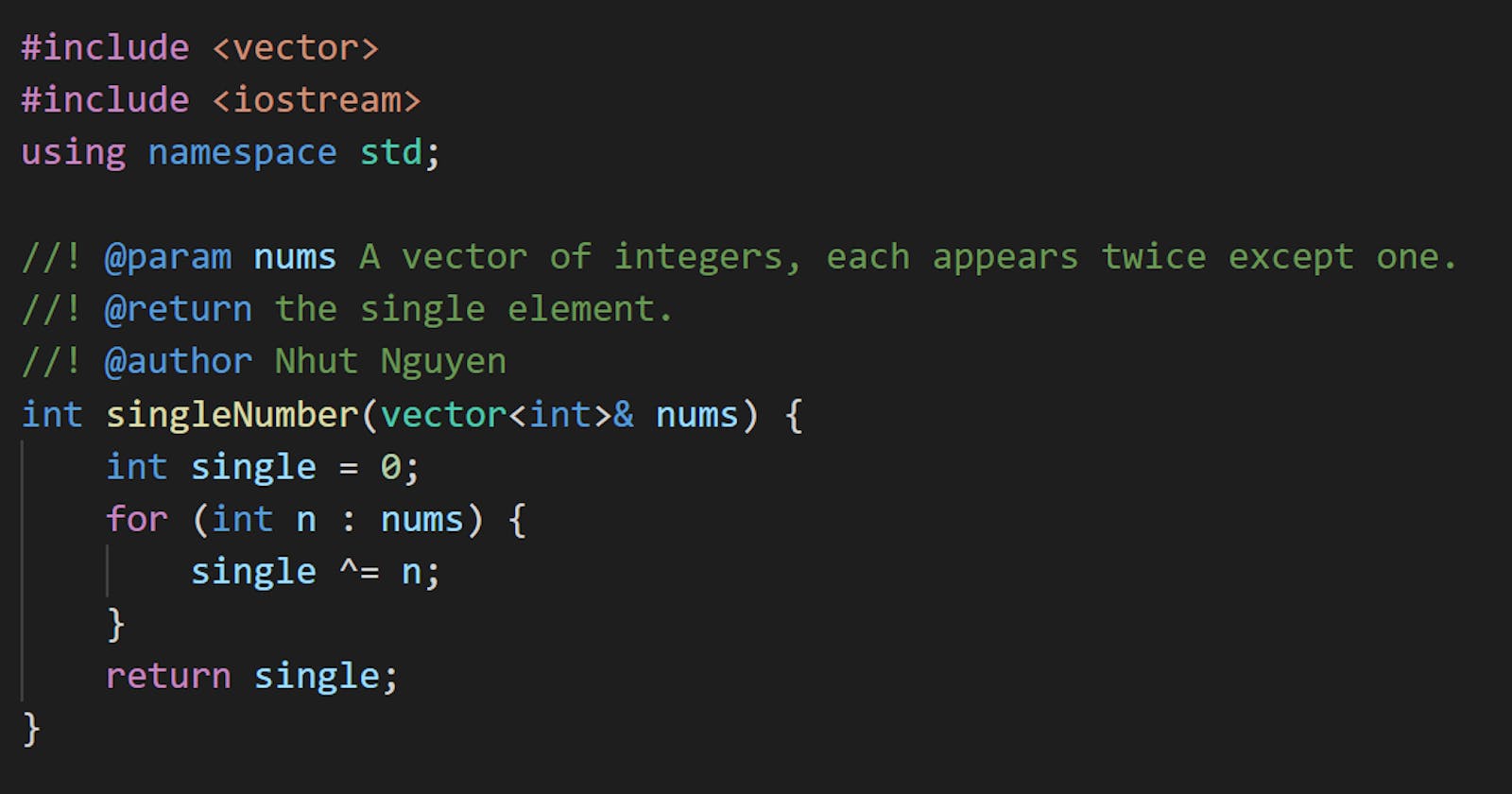
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int single = 0;
for (int n : nums) {
single ^= n;
}
return single;
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums{2,2,1};
cout << singleNumber(nums) << endl;
nums = {4,1,2,1,2};
cout << singleNumber(nums) << endl;
nums = {1};
cout << singleNumber(nums) << endl;
}
Output:
1
4
1
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N), whereN = nums.length.Extra space:
O(1).
References
Thanks for reading. Feel free to share your thought about my content and check out my FREE book “10 Classic Coding Challenges”.